Volleyball
Volleyball is an Olympic team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules.
The complete rules are extensive. But simply, play proceeds as follows: A player on one of the teams begins a 'rally' by serving the ball (tossing or releasing it and then hitting it with a hand or arm), from behind the back boundary line of the court, over the net, and into the receiving team's court. The receiving team must not let the ball be grounded within their court. They may touch the ball as many as three times. Typically, the first two touches are to set up for an attack, an attempt to direct the ball back over the net in such a way that the serving team is unable to prevent it from being grounded in their court.
The rally continues, with each team allowed as many as three consecutive touches, until either (1): a team makes a kill, grounding the ball on the opponent's court and winning the rally; or (2): a team commits a fault and loses the rally. The team that wins the rally is awarded a point, and serves the ball to start the next rally. A few of the most common faults include:

- causing the ball to touch the ground outside the opponents' court or without first passing over the net;
- catching and throwing the ball;
- double hit: two consecutive contacts with the ball made by the same player;
- four consecutive contacts with the ball made by the same team.
- net foul: touching the net during play.
The ball is usually played with the hands or arms, but players can legally strike or push (short contact) the ball with any part of the body.
A number of consistent techniques have evolved in volleyball, including spiking and blocking (because these plays are made above the top of the net the vertical jump is an athletic skill emphasized in the sport) as well as passing, setting, and specialized player positions and offensive and defensive structures.
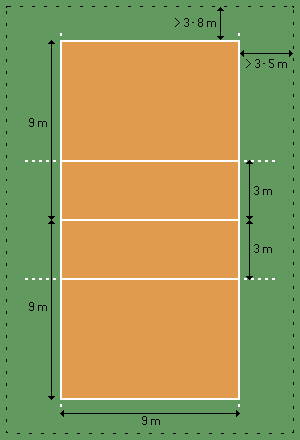
The court
The game is played on a volleyball court 18 meters (59 feet) long and 9 meters (29.5 feet) wide, divided into two 9 m × 9 m halves by a one-meter (40-inch) wide net placed so that the top of the net is 2.43 meters (7 feet 11 5/8 inches) above the center of the court for men's competition, and 2.24 meters (7 feet 4 1/8 inches) for women's competition (these heights are varied for veterans and junior competitions).
There is a line 3 meters from and parallel to the net in each team court which is considered the "attack line". This "3 meter" (or 10 foot) line divides the court into "back row" and "front row" areas (also back court and front court). These are in turn divided into 3 areas each: these are numbered as follows, starting from area "1", which is the position of the serving player:
After a team gains the serve (also known as siding out), its members must rotate in a clockwise direction, with the player previously in area "2" moving to area "1" and so on, with the player from area "1" moving to area "6".

The team courts are surrounded by an area called the free zone which is a minimum of 3 meters wide and which the players may enter and play within after the service of the ball. All lines denoting the boundaries of the team court and the attack zone are drawn or painted within the dimensions of the area and are therefore a part of the court or zone. If a ball comes in contact with the line, the ball is considered to be "in". An antenna is placed on each side of the net perpendicular to the sideline and is a vertical extension of the side boundary of the court. A ball passing over the net must pass completely between the antennae (or their theoretical extensions to the ceiling) without contacting them.
Volleyball (ball)
FIVB regulations state that the ball must be spherical, made of leather or synthetic leather, have a circumference of 65–67 cm, a weight of 260–280 g and an inside pressure of 0.30–0.325 kg/cm2.Other governing bodies have similar regulations.
Block
Blocking refers to the actions taken by players standing at the net to stop or alter an opponent's attack.
A block that is aimed at completely stopping an attack, thus making the ball remain in the opponent's court, is called offensive. A well-executed offensive block is performed by jumping and reaching to penetrate with one's arms and hands over the net and into the opponent's area. It requires anticipating the direction the ball will go once the attack takes place. It may also require calculating the best foot work to executing the "perfect" block.
The jump should be timed so as to intercept the ball's trajectory prior to it crossing over the net. Palms are held deflected downward about 45-60 degrees toward the interior of the opponents court. A "roof" is a spectacular offensive block that redirects the power and speed of the attack straight down to the attacker's floor, as if the attacker hit the ball into the underside of a peaked house roof.
By contrast, it is called a defensive, or "soft" block if the goal is to control and deflect the hard-driven ball up so that it slows down and becomes more easy to be defended. A well-executed soft-block is performed by jumping and placing one's hands above the net with no penetration into the opponent's court and with the palms up and fingers pointing backward.
Blocking is also classified according to the number of players involved. Thus, one may speak of single (or solo), double, or triple block.

Successful blocking does not always result in a "roof" and many times does not even touch the ball. While it’s obvious that a block was a success when the attacker is roofed, a block that consistently forces the attacker away from his or her 'power' or preferred attack into a more easily controlled shot by the defense is also a highly successful block.
At the same time, the block position influences the positions where other defenders place themselves while opponent hitters are spiking.
Pass
Also called reception, the pass is the attempt by a team to properly handle the opponent's serve, or any form of attack. Proper handling includes not only preventing the ball from touching the court, but also making it reach the position where the setter is standing quickly and precisely.
The skill of passing involves fundamentally two specific techniques: underarm pass, or bump, where the ball touches the inside part of the joined forearms or platform, at waist line; and overhand pass, where it is handled with the fingertips, like a set, above the head. Either are acceptable in professional and beach volleyball, however there are much tighter regulations on the overhand pass in beach volleyball.

Serve
A player stands behind the inline and serves the ball, in an attempt to drive it into the opponent's court. His or her main objective is to make it land inside the court; it is also desirable to set the ball's direction, speed and acceleration so that it becomes difficult for the receiver to handle it properly. A serve is called an "ace" when the ball lands directly onto the court or travels outside the court after being touched by an opponent.
In contemporary volleyball, many types of serves are employed:
- Underhand: a serve in which the player strikes the ball below the waist instead of tossing it up and striking it with an overhand throwing motion. Underhand serves are considered very easy to receive and are rarely employed in high-level competitions.
- Sky Ball Serve: a specific type of underhand serve occasionally used in beach volleyball, where the ball is hit so high it comes down almost in a straight line. This serve was invented and employed almost exclusively by the Brazilian team in the early 1980s and is now considered outdated. In Brazil, this serve is called Jornada nas Estrelas (Star Trek).
- Topspin: an overhand serve where the player tosses the ball high and hits it with a wrist span, giving it topspin which causes it to drop faster than it would otherwise and helps maintain a straight flight path. Topspin serves are generally hit hard and aimed at a specific returner or part of the court. Standing topspin serves are rarely used above the high school level of play.
- Float: an overhand serve where the ball is hit with no spin so that its path becomes unpredictable, akin to a knuckleball in baseball.
- Jump Serve: an overhand serve where the ball is first tossed high in the air, then the player makes a timed approach and jumps to make contact with the ball, hitting it with much pace and topspin. This is the most popular serve amongst college and professional teams.
- Jump Float: an overhand serve where the ball is tossed high enough that the player may jump before hitting it similarly to a standing float serve. The ball is tossed lower than a topspin jump serve, but contact is still made while in the air. This serve is becoming more popular amongst college and professional players because it has a certain unpredictability in its flight pattern.























Post a Comment